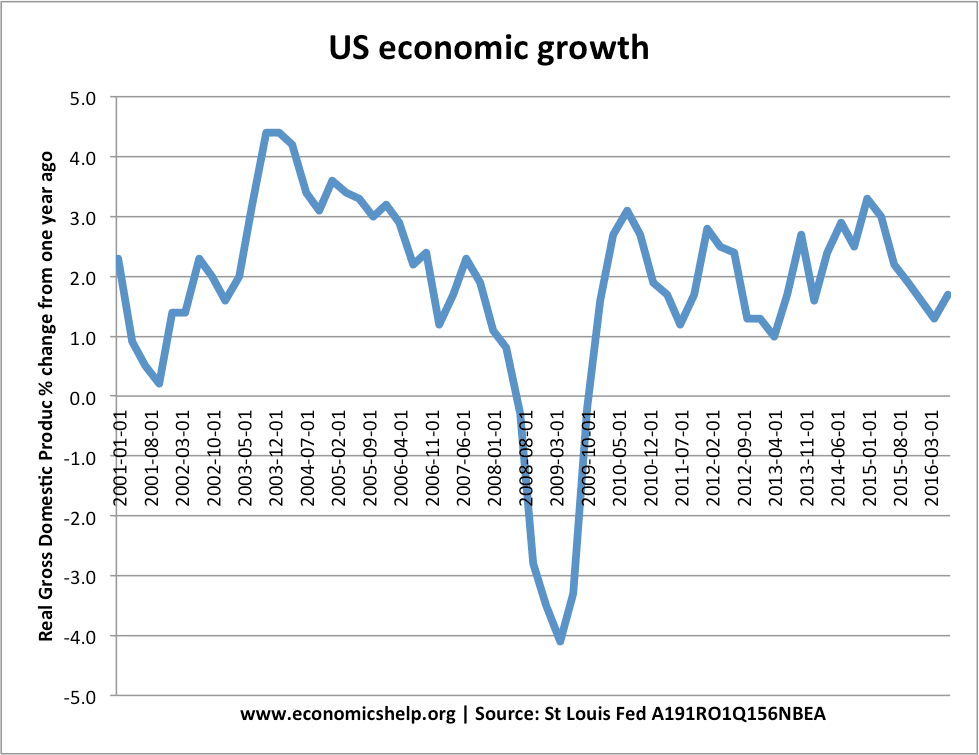
The U.S. economy recession outlook has become increasingly concerning as various factors converge, raising alarm bells among analysts and investors alike. With the ongoing trade war effects reverberating through key sectors, market volatility has thrived, further nudging the nation closer to potential recession. Investors are particularly worried about the Federal Reserve interest rates, which could shift dramatically in response to economic conditions and consumer confidence indices. Recent declines in the consumer sentiment index signal waning confidence among Americans, adding to discussions around the tariff impact on the economy and its broader implications for growth. As these developments unfold, policymakers face tough choices and the possibility of a slow and painful economic transition looms large on the horizon.
Examining the potential downturn in the American economy reveals a landscape fraught with uncertainty and potential pitfalls. Influential factors such as escalating international trade tensions, fluctuations in interest rates set by the Federal Reserve, and changing consumer attitudes contribute to this volatile environment. The repercussions of tariff policies not only resonate within domestic borders but also send ripples through global markets, affecting trade dynamics and economic health. As analysts evaluate the looming recession concerns, the changing perceptions of risk and market stability become central to the discourse of economic forecasting. Understanding the intricate interplay of these variables is crucial for grasping what lies ahead for the financial well-being of both businesses and consumers.
Current Prospects for the U.S. Economy
As we forecast the future of the U.S. economy, key indicators suggest a mix of challenges and potential recovery paths. The recent downturn in consumer sentiment, exemplified by the University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index, highlights mounting apprehension among consumers about their economic prospects. This decline in confidence can create a vicious cycle; if consumers are worried, they’ll likely spend less, which in turn can slow down economic growth. Consequently, as consumer spending is a critical component of the GDP, further dips in sentiment could lead the economy closer to a recession.
Moreover, the looming threats of a long-term trade war and its corresponding tariffs have exacerbated uncertainties within the economy. With countries retaliating against U.S. tariffs, businesses face increased costs which may be passed down to consumers. This scenario amplifies fears of rising inflation, while simultaneously hindering both domestic and foreign investments. Analysts are paying close attention to how these factors interplay, as they could lead to more significant shifts in economic performance than anticipated.
Impact of Trade Wars on Economic Stability
The current trade wars significantly impact the U.S. economy, igniting fears of recession among economists and financial analysts. Tariffs imposed on American goods not only provoke retaliation from international partners but can also lead to increased costs for U.S. companies that rely on imported materials. This uptick in prices can contribute to inflationary pressures, further straining household budgets and dampening consumer spending, which is vital for economic growth. The Federal Reserve is caught in this predicament where they must balance potential inflation with the need to support economic stability.
Moreover, the long-term implications of prolonged trade disputes could be dire. Businesses, particularly small and medium enterprises, are already expressing caution by halting hiring and deferring investments due to an uncertain market landscape. These decisions can lead to a significant slowdown in economic activity. Without robust consumer spending and business investment, the risk of entering a recession may escalate, which is a concern expressed by several economists observing current market conditions.
The Role of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve (Fed) plays a pivotal role in determining the trajectory of the U.S. economy, particularly through its setting of interest rates. As the nation grapples with inflationary concerns and a sluggish consumer sentiment index, the Fed faces a challenging decision-making process. On one hand, cutting interest rates can stimulate economic activity by reducing borrowing costs, thereby encouraging consumer spending and business investments. On the other hand, these actions must be tempered with caution to avoid exacerbating inflation, which has been rising in part due to the effects of tariffs and supply chain disruptions.
Given these complexities, there is a growing discourse about potential outcomes from the Fed’s decisions in the coming months. Should they maintain or lower interest rates in light of deteriorating economic indicators, such as a declining consumer sentiment and fears of a recession? The implications of these decisions extend beyond immediate economic indicators; they influence investor confidence and the overall economic environment, which is particularly at risk during turbulent periods marked by trade wars and shifting fiscal policies.
Consumer Sentiment Index: A Recession Indicator?
The University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index has been a crucial bellwether for gauging public confidence in the economy. Recent trends indicate that sentiment has plummeted to levels not seen since late 2022, indicating significant concerns among consumers regarding their economic well-being and the broader economic prospects. A declining sentiment index often translates to reduced consumer spending, which can aggravate economic slowdowns and potentially lead to a recession. This signals a worrying trend, as consumer confidence generally acts as a precursor to economic growth or decline.
Furthermore, the correlation between consumer sentiment and spending behavior cannot be overstated. When consumers feel optimistic, they are more likely to make purchases, which fuels economic growth. Conversely, a lack of confidence can lead to decreased expenditure, impacting everything from retail sales to housing markets. When consumers retreat into saving mode, the ripple effects can lead to a slowdown in economic activity, raising serious questions about the durability of the U.S. economy amidst a backdrop of escalating trade tensions and potential fiscal crises.
The Long-term Economic Effects of Tariffs
The implementation of tariffs has shown to have far-reaching effects on both micro and macroeconomic levels. While proponents may argue that tariffs protect domestic industries from foreign competition, the immediate result is often increased prices for consumers and decreased market efficiency. Economists widely recognize that a trade barrier disrupts the market equilibrium, leading to inefficiencies that could inhibit growth in the long term. Industries dependent on global supply chains are particularly vulnerable to these disruptions, which can further diminish overall economic performance.
In light of the current trade wars, businesses are adapting to the new reality by either passing costs onto consumers or absorbing the financial hit. Both scenarios can lead to reduced profitability, which can hinder expansion and job creation. Additionally, prolonged tariffs may provoke retaliatory measures from trading partners, potentially escalating into a full-blown trade conflict that only compounds existing economic troubles. The rapid shifts in trade policy not only shake consumer confidence but also discourage international investments that are critical for a resilient economy.
Political Uncertainty: Effects on Economical Confidence
Political uncertainty can trigger economic instability, particularly in a climate influenced by erratic government policies and trade confrontations. The present administration’s unpredictable approach to tariffs has raised questions about fiscal responsibility and long-term economic strategy. Investors are increasingly cautious, adjusting their economic forecasts with each policy announcement. The resultant instability contributes to a climate in which consumers may restrain spending, fearing potential negative economic ramifications from policy changes.
As uncertainty looms, businesses are forced to adopt a wait-and-see approach, further stymying economic momentum. Hiring freezes and reduced capital investments become common as firms prioritize risk management over expansion. Analysts argue that this hesitation is detrimental to building a sustainable economy, as a lack of proactive investment can stifle growth and innovation. Therefore, the economic outlook appears bleak if political stability does not improve, potentially leading the nation into a recession.
Analyzing the Potential for Future Recession
The fear of a coming recession in the U.S. economy has gained traction among economists, especially given the confluence of various destabilizing factors. Increased risks from trade wars, inflationary pressures due to tariffs, and a cooling labor market contribute to an atmosphere ripe for economic downturn. If the Federal Reserve does not navigate carefully between inflation and stagnation, the conditions for a recession could be set in motion. This precarious situation underscores the importance of closely monitoring key economic indicators.
Moreover, the indicators suggesting a an imminent recession are numerous, including a sharp decline in the consumer sentiment index and significant market volatility. Economists point out that each sign of weakening confidence can have a cascading effect, leading to reduced consumption and business investment. Without decisive action, the interconnectedness of these factors suggests that the U.S. economy may indeed slip into recession if these trends do not reverse.
Economic Predictions and Future Scenarios
In forecasting the U.S. economy, various economic models indicate several potential scenarios influenced by current domestic and international events. With tariffs impacting trade relationships and constraining business operations, forecasters stress the need for adaptive economic policies. A key part of mitigating recession risks lies in devising strategies that shift the economic focus from punitive tariffs to constructive negotiations, thus fostering a healthier trade environment and alleviating tensions.
Additionally, strategies surrounding fiscal policy and consumer stimulation will play vital roles in shaping future economic outcomes. Policymakers must create conditions conducive to sustainable growth, perhaps by reassessing the current tariff structure and exploring ways to reinvigorate consumer confidence. The ability of the economy to emerge resilient from current challenges will rely heavily on coordinated actions aimed at stabilizing markets and encouraging investment, ultimately steering the U.S. towards a more promising economic horizon.
The Federal Reserve’s Balancing Act: Interest Rates and Economic Growth
Navigating the intersection of interest rates and economic growth is a persistent challenge for the Federal Reserve, particularly during tumultuous economic periods characterized by trade wars and investor uncertainty. The Fed faces intense pressure to decide between lowering interest rates to stimulate growth or maintaining them to control inflation. Each of these choices carries significant repercussions for the wider economy, impacting everything from consumer spending to the housing market, as well as long-term investment strategies.
The ramifications of the Fed’s decisions extend beyond just immediate economic conditions; they also shape investor perceptions and market stability. If consumers and businesses perceive that the Fed is effectively managing inflation while fostering growth through strategic interest rate policies, confidence can stabilize and potentially flourish despite external pressures. However, any missteps in policy direction could exacerbate existing economic vulnerabilities, leading to a downturn that needs careful navigation to avoid further recession.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current outlook for a U.S. economy recession based on the latest consumer sentiment index?
The current outlook for a U.S. economy recession appears to be concerning, as the University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index has dropped to its lowest level since November 2022. This decline in consumer confidence, combined with factors like ongoing trade war effects and potential stock market volatility, raises alarms about a possible recession in the near future.
How are Federal Reserve interest rates playing a role in the U.S. economy recession outlook?
Federal Reserve interest rates are crucial to the U.S. economy recession outlook. The Fed faces a dilemma: cutting rates could support the economy and employment, while maintaining rates could help control inflation. In the current climate of trade wars and economic uncertainty, the Fed is likely to keep rates unchanged, which may not sufficiently stimulate growth needed to avoid a recession.
What impact does the trade war have on the U.S. economy recession outlook?
The ongoing trade war significantly impacts the U.S. economy recession outlook. Tariffs imposed on American goods by countries like China, Mexico, and Canada could lead to reduced consumer spending, increased production costs, and a slowdown in trade. These factors create an atmosphere of uncertainty, which can heighten the risk of a recession.
Is the U.S. economy heading towards stagflation due to recent economic indicators?
The combination of high inflation, low consumer sentiment, and stagnating wages raises concerns that the U.S. economy could face stagflation, reminiscent of the 1970s. The current economic indicators suggest that if corrective measures are not taken, a recession may occur alongside stagnant economic growth and rising prices.
What are the main factors contributing to the U.S. economy recession outlook?
Key factors contributing to the U.S. economy recession outlook include the trade war effects leading to reduced market confidence, diminished consumer sentiment, and volatility in the stock market. Furthermore, potential cuts in government spending and rising perceptions of economic risk further exacerbate the likelihood of a recession in the near term.
How does consumer sentiment affect the U.S. economy recession outlook?
Consumer sentiment is a critical component of the U.S. economy recession outlook. When consumers feel less confident about their financial situation, they are less likely to spend, which can lead to reduced economic growth and increased recession risks. The latest drop in the consumer sentiment index indicates a potentially declining economic environment.
What role does tariff impact on economy play in predicting the U.S. economy recession?
The tariff impact on the economy is significant in predicting the U.S. economy recession, as tariffs can increase prices for consumers and limit trade. This, combined with the uncertainty it creates in the market, can lead to slower economic growth and heighten the risk of a recession, especially if the trade tensions continue or escalate further.
What can be expected from the Federal Reserve regarding interest rates amidst the recession outlook for the U.S. economy?
Given the current recession outlook for the U.S. economy, the Federal Reserve is expected to carefully consider its options regarding interest rates. While they may recognize the need to support economic growth through potential rate cuts, the rising inflation and volatility from trade wars may lead them to maintain current rates to avoid further complicating the economic situation.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Trade War Concerns | Heavy losses in U.S. markets due to tariffs imposed by China, Mexico, and Canada. |
| Consumer Sentiment | University of Michigan’s index has dropped to its lowest since November 2022. |
| Potential for Recession | Economist Jeffrey Frankel warns of higher likelihood of recession, citing trade war, stock market, and fiscal crises. |
| Market Reactions | Market selloff characterized as a ‘normal correction’ but raises concerns about future economic stability. |
| Federal Reserve’s Dilemma | Fed may not change interest rates due to conflicting concerns about inflation and economic slowdown. |
Summary
The U.S. economy recession outlook is increasingly concerning as market volatility and declining consumer sentiment point towards a challenging economic environment. With the trade war escalating and Federal Reserve policies in flux, many analysts predict that the likelihood of a recession within the next year has grown significantly. The interplay between governmental fiscal strategies and consumer confidence will be critical in determining the eventual economic trajectory.