Housing construction productivity is a pressing issue at the heart of America’s current housing crisis, exacerbated by stringent land-use regulations and pervasive NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies. These policies have stifled innovation within the construction sector, leading to a dramatic decline in the efficiency of home-building practices. As housing prices soar, more Americans find homeownership increasingly unattainable, resulting in significant affordability issues. In fact, over the past several decades, the cost of new homes has more than doubled, primarily due to rising labor and material costs compounded by regulatory barriers. Addressing these challenges requires a critical look at the interplay between regulatory practices and construction productivity, as the industry grapples with the need for innovation and scalable solutions.
The current landscape of the housing sector reflects significant hurdles in construction efficiency, driven by restrictive local policies and community resistance. These factors contribute to a slowdown in the development of new residential units, despite an urgent demand for affordable housing. The juxtaposition of modern challenges with historical efficiencies highlights a troubling trend in the production of homes that many see as an indicator of broader societal issues. As land-use mandates grow more complex, new approaches to building and design are being hindered, creating barriers not just to homeownership but also to societal growth. This paradigm shift in housing dynamics necessitates a reevaluation of regulatory frameworks to foster an environment conducive to innovation and increased productivity.
The Impact of NIMBYism on Housing Construction Productivity
NIMBY (Not In My Back Yard) policies have increasingly influenced housing construction productivity in America, creating a significant barrier in addressing the ongoing housing crisis. These land-use regulations often restrict large-scale building projects, stifling the potential for mass production that could drive down costs. Consequently, builders are left with no choice but to engage in smaller, bespoke developments, thereby decreasing their overall productivity. The evidence suggests that as NIMBY policies have grown in prominence, the housing sector’s ability to innovate and operate efficiently has diminished, leading to higher housing costs that outstrip wage growth.
The correlation between NIMBY policies and housing construction productivity is stark. A recent study shows that as local regulations became tighter, the number of housing starts per worker plummeted, showcasing a 40% decline in productivity since 1970. This shift indicates a departure from the once-flourishing era of mass housing developments where economies of scale facilitated cost-effective solutions. With builders now navigating a maze of zoning laws and community stipulations, the industry’s response has often been to retreat to smaller projects that lack the innovation and efficiency found in larger-scale operations.
Housing Crisis in America: Causes and Consequences
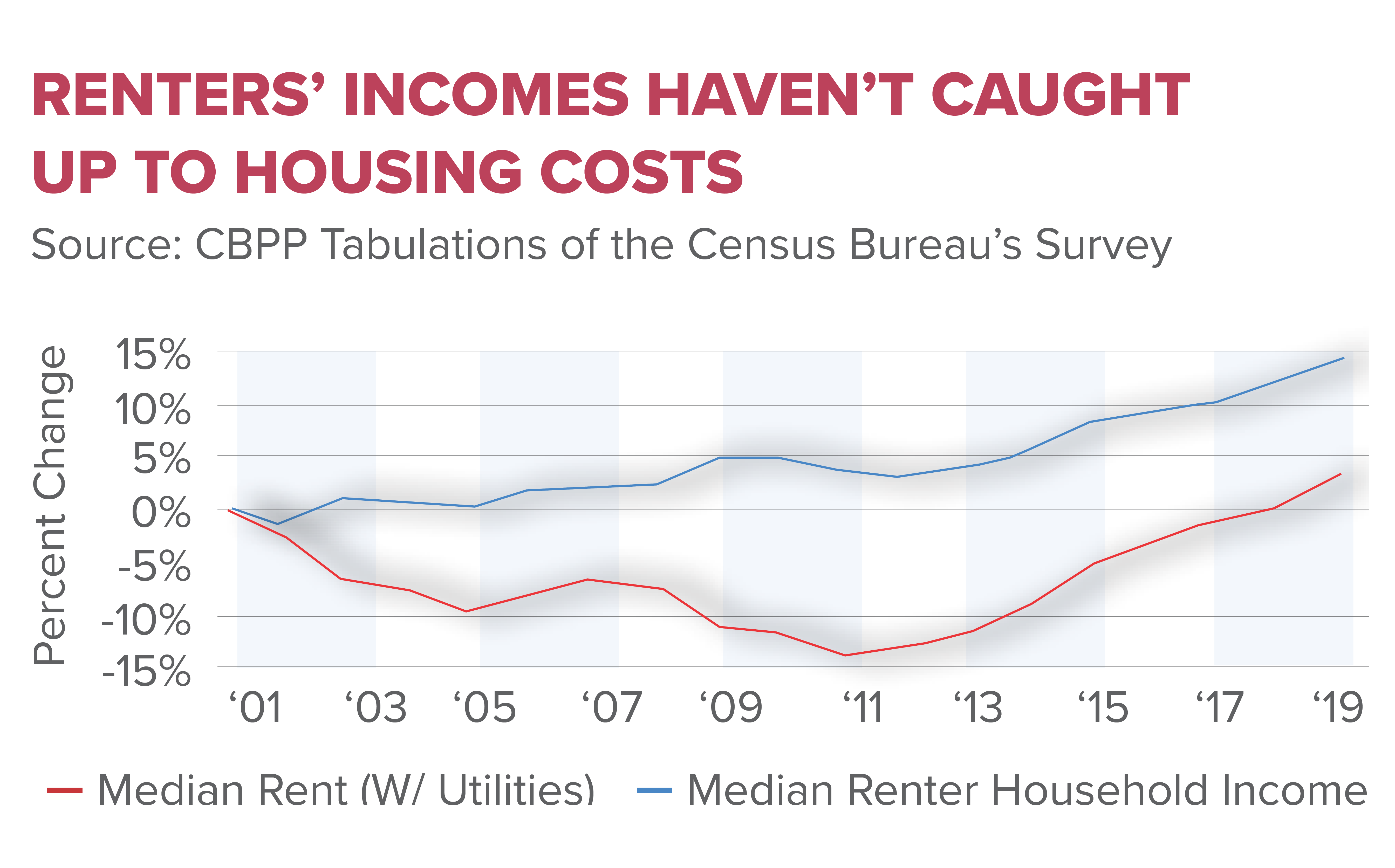
The housing crisis in America is a complex issue shaped by various factors, including economic disparities and restrictive land-use regulations. As housing prices continue to soar, affordability remains a paramount concern for many families. With the cost of a new single-family home having more than doubled since 1960, it is no wonder that a significant portion of the population finds homeownership increasingly unattainable. These affordability issues are exacerbated by local regulations that discourage investment in large-scale housing projects, further limiting the supply needed to meet demand.
The consequences of the housing crisis extend beyond simple affordability; they also impact overall economic vitality and social stability in communities. The inability to provide affordable housing contributes to a growing wealth gap, as younger generations struggle to build equity while their older counterparts enjoy the benefits of real estate ownership. This dynamic reinforces the cycle of inequality, shrinking opportunities, and driving homeownership further out of reach for many. As policymakers grapple with these challenges, addressing the roots of the housing crisis will require a comprehensive approach that includes reforming land-use regulations and promoting innovative construction practices.
Innovations in the Construction Sector: A Necessity for Progress
In the face of declining productivity, innovation within the construction sector is essential for revitalizing housing development in America. Historically, the construction industry mirrored trends seen in manufacturing, with tremendous advancements fueling productivity and cost-efficiency. However, since the 1970s, construction has seen a noticeable drop in its patenting activity and research investments, which indicates a stagnation in innovation compared to other sectors. This stagnation ultimately translates to higher construction costs and slower project completions, which has long-term implications for the housing market.
To combat this decline in innovation and productivity, the construction sector must embrace new technologies and methods that streamline processes and lower costs. For instance, modular construction, prefabrication, and innovative materials could all play significant roles in reshaping how homes are built. By promoting these advancements, the construction industry can begin to recover its former productivity levels, ultimately contributing to larger housing projects that can alleviate some of the pressures inherent in the current housing crisis. Thus, fostering an environment conducive to innovation is critical for both builders and the communities they serve.
Addressing Affordability Issues in Housing Through Policy Changes
Tackling the affordability issues in housing demands a multifaceted approach that includes significant policy changes at local and state levels. One key area for reform is the review and adjustment of existing land-use regulations that currently inhibit the development of affordable housing. By loosening these constraints, governments can encourage larger-scale housing projects, increasing the supply of homes available at a lower price point. This would help mitigate the effects of NIMBY-ism, which has historically stymied the construction of much-needed housing developments.
Additionally, policies that promote mixed-use developments and encourage higher-density construction can significantly improve the availability of affordable housing. By integrating residential spaces with commercial and recreational areas, cities can foster vibrant communities that attract diverse demographics. Such policy shifts not only address affordability but can also positively influence local economies by creating jobs and increasing property values. Ultimately, rethinking land-use policies is fundamental to reversing affordability trends and ensuring future generations can access affordable housing options.
The Role of Government in Housing Development
Government plays a pivotal role in housing development, particularly in regulating construction practices and ensuring equitable access to housing. As policymakers navigate the complexities of land-use regulations, they must strike a balance between community interests and the pressing need for affordable housing. A transparent and streamlined approval process can facilitate the timely development of new projects, enabling builders to respond more rapidly to the changing housing market. Without proactive government action, the constraints imposed by NIMBY policies will continue to hamper housing construction productivity.
Moreover, government investment in infrastructure and zoning reform can catalyze positive change in the housing sector. By incentivizing larger developments and easing bureaucratic hurdles, local governments can significantly impact housing supply and affordability. Collaboration between public and private sectors is crucial to develop sustainable housing solutions that meet the needs of diverse populations, particularly in urban areas facing critical shortages. A proactive government approach can not only amplify housing construction productivity but also improve overall community resilience and economic growth.
Encouraging Community Engagement in Housing Initiatives
Engaging communities in housing initiatives is essential for overcoming resistance to new developments often expressed through NIMBY sentiments. Through open forums, educational outreach, and proactive communication, builders and local governments can address community concerns and foster a more collaborative approach to housing development. By involving residents in the planning process, stakeholders can gain insights into local priorities and preferences that align with broader housing goals, resulting in projects that are both welcomed and needed.
Furthermore, active community engagement can enhance the public perception of new housing initiatives, shifting the narrative from opposition to acceptance. When residents feel their voices are heard and considered, they are more likely to support developments that, while potentially impactful on their landscape, are vital for addressing larger housing affordability and accessibility issues. By building trust and encouraging collaboration, communities can collectively navigate the complexities of housing development, leading to sustainable solutions that benefit everyone.
Understanding the Economics of Housing Supply and Demand
The dynamics of housing supply and demand are essential factors in understanding the broader housing market, particularly concerning affordability. As demand for housing increases with population growth and urbanization, supply must keep pace to prevent significant price escalations. However, restrictive land-use policies and the prevailing NIMBY mindset have inhibited the construction of sufficient housing units, creating a gap that exacerbates affordability issues. This imbalance highlights the urgent need to reassess existing regulations to promote a healthier—more balanced—housing market.
Furthermore, understanding economic theories surrounding supply and demand can help policymakers formulate effective strategies to alleviate inflationary pressures in housing costs. Encouraging new residential developments and increasing housing stock can moderate surging prices, making homeownership more accessible to the average American. Ultimately, tackling these economic fundamentals is an integral part of resolving the housing crisis and catalyzing a productive pathway for future growth in the construction sector.
Long-Term Solutions for the Housing Affordability Crisis
Finding long-term solutions for the housing affordability crisis necessitates a comprehensive strategy that incorporates various stakeholders across sectors. Solutions may include revisiting zoning laws, stimulating public-private partnerships, and advocating for innovative building practices that increase efficiency and reduce costs. By removing barriers to large projects and investing in infrastructure improvements, communities can enhance their housing capacity without compromising quality or accessibility. These proactive measures are essential as the nation grapples with both the immediate and lingering effects of the housing crisis.
Additionally, education and advocacy surrounding the importance of affordable housing must play a vital role in the conversation about long-term solutions. Empowering communities with knowledge around the economic and social benefits of housing development can foster a more supportive environment for new initiatives. By engaging residents as allies rather than adversaries, housing projects can be positioned as integral components of community growth, ultimately contributing to a more inclusive and equitable society.
The Future of Housing Construction in America: Trends and Predictions
As we look to the future, the landscape of housing construction in America is expected to evolve significantly. Current trends indicate a shift towards sustainable building practices and smart home technologies that prioritize energy efficiency and lower operating costs. These innovations not only address environmental concerns but also cater to a growing consumer base interested in sustainability—a factor that could influence future housing preferences and construction practices. The integration of technology in construction is poised to enhance productivity and streamline processes, positioning the sector for a necessary rebound.
Moreover, the future of housing construction will likely depend on overcoming the challenges posed by NIMBY policies and outdated land-use regulations. As awareness of the necessity for affordable housing mounts, communities may push for reforms that enable faster, more comprehensive development solutions. This shift could herald a renaissance in housing affordability, blending traditional practices with modern innovations. Ultimately, by embracing change and fostering collaborative relationships among stakeholders, the construction industry can better meet the demands of the future and ensure that housing is accessible for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do NIMBY policies impact housing construction productivity?
NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies significantly undermine housing construction productivity by imposing restrictive land-use regulations that limit the scale and scope of housing projects. These restrictions often lead to smaller developments, which do not benefit from economies of scale. Consequently, builders are forced to micromanage projects and produce bespoke homes, resulting in decreased innovation and higher costs, exacerbating the housing affordability crisis.
What is the relationship between land use regulation and the housing crisis in America?
Land use regulations play a crucial role in the ongoing housing crisis in America. Tighter controls have reduced construction productivity, leading to fewer housing starts and higher costs for new homes. This regulatory environment discourages large-scale building projects, which are essential for achieving lower costs through mass production. As a result, the affordability issues in housing are intensified, making homeownership increasingly unattainable for many.
Why has housing construction productivity declined since the 1970s?
Since the 1970s, housing construction productivity has declined primarily due to the rise of stringent land-use regulations and NIMBY policies. These regulations have restricted the ability of builders to undertake large-scale developments, leading to smaller, less efficient projects. Additionally, the decline in the size of construction firms has decreased their incentive to innovate, further hampering productivity in the housing sector.
What are the effects of construction sector innovation on housing affordability?
Construction sector innovation directly impacts housing affordability by enabling builders to reduce costs and increase efficiency. However, a stagnation in innovation, attributed to restrictive land-use regulations and the prevalence of small-scale projects, has led to skyrocketing home prices. Without significant innovation, the construction industry struggles to address the substantial demand for affordable housing, worsening the affordability crisis.
How does housing construction productivity affect the availability of affordable housing?
Housing construction productivity affects the availability of affordable housing by determining how efficiently homes can be built and how many can be produced to meet demand. Declining productivity, driven by land-use regulations and NIMBY policies, results in fewer homes and higher prices. Consequently, the supply of affordable housing diminishes, making it increasingly difficult for many Americans to access affordable living options.
| Key Points |
|---|
| U.S. housing construction productivity has declined significantly since 1970, coinciding with stricter land-use regulations. |
| The rise of NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies restricts large-scale housing development, leading to smaller projects and firms, reducing efficiency. |
| Housing prices have more than doubled since 1960, contributing to a national housing affordability crisis. |
| Large construction firms (500+ employees) produce four times more housing units per employee compared to smaller firms. |
| Patent activity in the construction sector has declined since the 1970s, indicating a lack of innovation in housing construction. |
| Economic disparity in housing wealth has widened, affecting potential first-time homebuyers significantly across generations. |
Summary
Housing construction productivity has faced major challenges over recent decades, primarily due to increasing land-use regulations and the proliferation of NIMBYism. This has led to less innovation and a shift towards smaller building projects, exacerbating the affordability crisis in housing. Understanding the relationship between these factors is essential for realigning housing construction productivity with broader economic trends and ensuring that homeownership becomes attainable for more Americans.