Entrepreneurialism has emerged as a defining force in the modern era, transforming how individuals relate to work and their careers. In this dynamic landscape, many are embracing the concept of ‘make your own job,’ which empowers them to take control of their professional journeys. This shift towards self-employment fosters a vibrant freelance economy, allowing for a diverse range of opportunities that cater to personal skills and passions. As the entrepreneurial mindset permeates contemporary work culture, it inspires individuals to innovate and thrive in environments that prioritize autonomy and creativity. However, this drive for entrepreneurialism often brings challenges, with many navigating the fine line between ambition and the pressures of constant self-promotion and competition.
The rise of entrepreneurial culture reflects a broader shift towards individualism and innovation in the workforce, often referred to by terms such as self-entrepreneurship or the gig economy. This change encourages professionals across various sectors to redefine traditional employment norms and create opportunities tailored to their unique skill sets. With the advent of remote work and technology-driven platforms, many are becoming solopreneurs or freelance workers, actively participating in a robust economy that values agility and adaptability. Today’s modern work environment promotes an entrepreneurial spirit, pushing individuals to embrace risks and cultivate an entrepreneurial mindset that aligns with their personal and professional aspirations. As we navigate this evolving landscape, the blending of entrepreneurship and conventional careers continues to shape the future of work.
The Rise of Entrepreneurialism in Modern Work Culture
In today’s rapidly evolving work landscape, the rise of entrepreneurialism is a significant trend reshaping what it means to work. With the advent of technology and an increasingly competitive market, more individuals are finding themselves stepping into entrepreneurial roles, whether it’s starting their own business, freelancing, or becoming influencers. This shift reflects the changing nature of work, where the traditional 9-to-5 job is no longer the only path to financial stability. The freelance economy offers unprecedented flexibility, allowing workers to tailor their careers around their life needs rather than conform to outdated corporate structures.
The embrace of entrepreneurialism also speaks to a deeper desire for autonomy and personal fulfillment in our work lives. As Erik Baker explores in “Make Your Own Job,” this trend is not merely a financial necessity but a profound cultural shift towards self-empowerment. Workers are increasingly motivated by the idea of ‘making their own job,’ a concept that encourages leveraging personal skills and passions to create fulfilling career paths. This entrepreneurial mindset fosters innovation and creativity, appealing to those who crave ownership of their professional destinies.
Navigating Self-Employment in a Gig Economy
Self-employment is becoming an increasingly viable option for many individuals who seek flexibility and independence in their careers. In a gig economy fueled by technology platforms, people can access numerous opportunities ranging from freelance graphic design to ride-sharing. This shift empowers individuals to pursue multiple passions, allowing them to build diverse income streams. However, while self-employment offers many rewards, it also introduces new challenges such as inconsistent income and lack of job security that traditional employment once provided.
Furthermore, navigating self-employment requires adopting an entrepreneurial mindset, where resilience and adaptability are crucial to success. As popularized by self-help authors throughout history, the drive for self-sufficiency demands not only the identification of opportunities but also strategic planning and execution. Self-employed individuals must continuously develop their skills, market themselves effectively, and manage the complexities of running their own businesses, which can be daunting yet ultimately rewarding.
The Influence of the Entrepreneur Mindset on Personal Development
The entrepreneurial mindset has transcended traditional notions of business success, becoming a cornerstone of personal development. This way of thinking encourages individuals to view obstacles as opportunities for growth. Erik Baker’s examination of America’s shift towards entrepreneurialism highlights how adopting this mindset can lead to increased resilience, creativity, and problem-solving abilities. This perspective is not confined to corporate environments; it permeates multiple aspects of life, fostering a culture of innovation regardless of one’s chosen career path.
Moreover, this mindset propels individuals to take charge of their destinies, inspiring them to constantly seek out new skills and knowledge. In a world where job security is increasingly uncertain, individuals are motivated to cultivate expertise, making them adaptable in the face of challenges. By embracing an entrepreneurial outlook, people can create a fulfilling professional life that aligns with their passions, contributing to both personal and societal advancements in modern work culture.
Freelance Economy: Opportunities and Challenges
The freelance economy continues to expand, presenting both remarkable opportunities and significant challenges for today’s workforce. With technology enabling seamless communication and collaboration, freelancers can work with clients across the globe, providing services in various fields from writing to consulting. This newfound flexibility allows individuals to set their own schedules, choose their projects, and achieve a better work-life balance than traditional employment often allows.
However, this ocean of opportunity is not without its turbulence. Freelancers face challenges such as inconsistent income, lack of health benefits, and the pressure of self-employed taxes. The uncertainty of not having a regular paycheck can be anxiety-inducing, making financial planning crucial. For many, the allure of freedom in the freelance economy is often balanced with the reality of navigating a competitive landscape filled with uncertainties. As such, those looking to thrive in this ecosystem must adopt robust entrepreneurial practices and build networks to secure stability.
How Modern Work Culture Shapes the Entrepreneurial Spirit
Modern work culture plays a pivotal role in fostering the entrepreneurial spirit across various industries. In an age where innovation is paramount, workplaces are increasingly designed to encourage creativity and collaboration. Companies such as Google and Apple epitomize environments that promote entrepreneurial thinking among employees, fostering a culture where ideas are not only welcomed but celebrated. This trend creates an atmosphere of shared responsibility and motivation, leading to a more engaged and productive workforce.
Furthermore, the rise of remote work tools and platforms has dismantled geographical barriers, allowing talented individuals from diverse backgrounds to contribute to entrepreneurial ventures. As organizations evolve, they prioritize hiring individuals with an entrepreneurial mindset, recognizing the value of proactive problem solvers. This cultural shift encourages employees to bring their ideas to the forefront, reinforcing the notion that anyone within an organization can be an entrepreneur, thus expanding the definition and reach of entrepreneurialism in contemporary work.
Embracing Change in an Entrepreneurial Landscape
Embracing change is essential in today’s entrepreneurial landscape, where technological advancements and evolving market trends can alter the course of careers overnight. The ability to pivot and adapt has become a hallmark of successful entrepreneurs, distinguishing those who thrive from those who struggle to keep pace. Erik Baker highlights how the historical shifts towards entrepreneurialism have equipped individuals with the mindset necessary to embrace change as a constant in their work lives.
In practical terms, this means continuously seeking knowledge and staying aware of industry innovations. Learning from failures, seeking mentorship, and networking with other professionals can enhance one’s adaptability and resilience in a dynamic work environment. Ultimately, those who embrace change position themselves as leaders in their fields, capable of innovating and finding their niche amidst the uncertainty that defines modern work.
The Role of Self-Help Literature in Shaping Entrepreneurialism
Self-help literature has a profound impact on shaping the contemporary understanding of entrepreneurialism. Books and resources that promote self-improvement and personal achievement have fueled the aspirations of countless individuals seeking to embark on their entrepreneurial journeys. The works of Napoleon Hill and others have instilled the belief that anyone can succeed by cultivating the right mindset and harnessing their unique skills.
These literary contributions encourage readers to view obstacles as opportunities and failures as stepping stones toward success. By providing practical advice and inspiring stories, self-help resources empower individuals to make actionable changes in their lives, fostering a culture of entrepreneurship. As people turn to these texts for motivation and strategy, self-help literature continues to inform the narrative around self-employment and the drive for economic independence in an ever-changing work ecosystem.
Building a Sustainable Business in the Entrepreneurial Era
Building a sustainable business is at the forefront of entrepreneurial discussions in today’s economy. As consumers increasingly value sustainability and ethical practices, entrepreneurs must not only seek profitability but also consider their impact on society and the environment. This paradigm shift is reshaping the expectations of businesses, encouraging entrepreneurs to incorporate sustainable practices from the outset in order to thrive.
In this era, sustainability is synonymous with innovation. Entrepreneurs are finding innovative ways to reduce waste, utilize renewable resources, and create value in ways that resonate with conscious consumers. By emphasizing ethical practices and accountability, today’s entrepreneurs can differentiate themselves in the crowded marketplace. Those who embrace sustainability as a core business principle stand to gain not only a competitive edge but also vital support from consumers looking to invest in a future that aligns with their values.
The Interconnection Between Unemployment and Entrepreneurialism
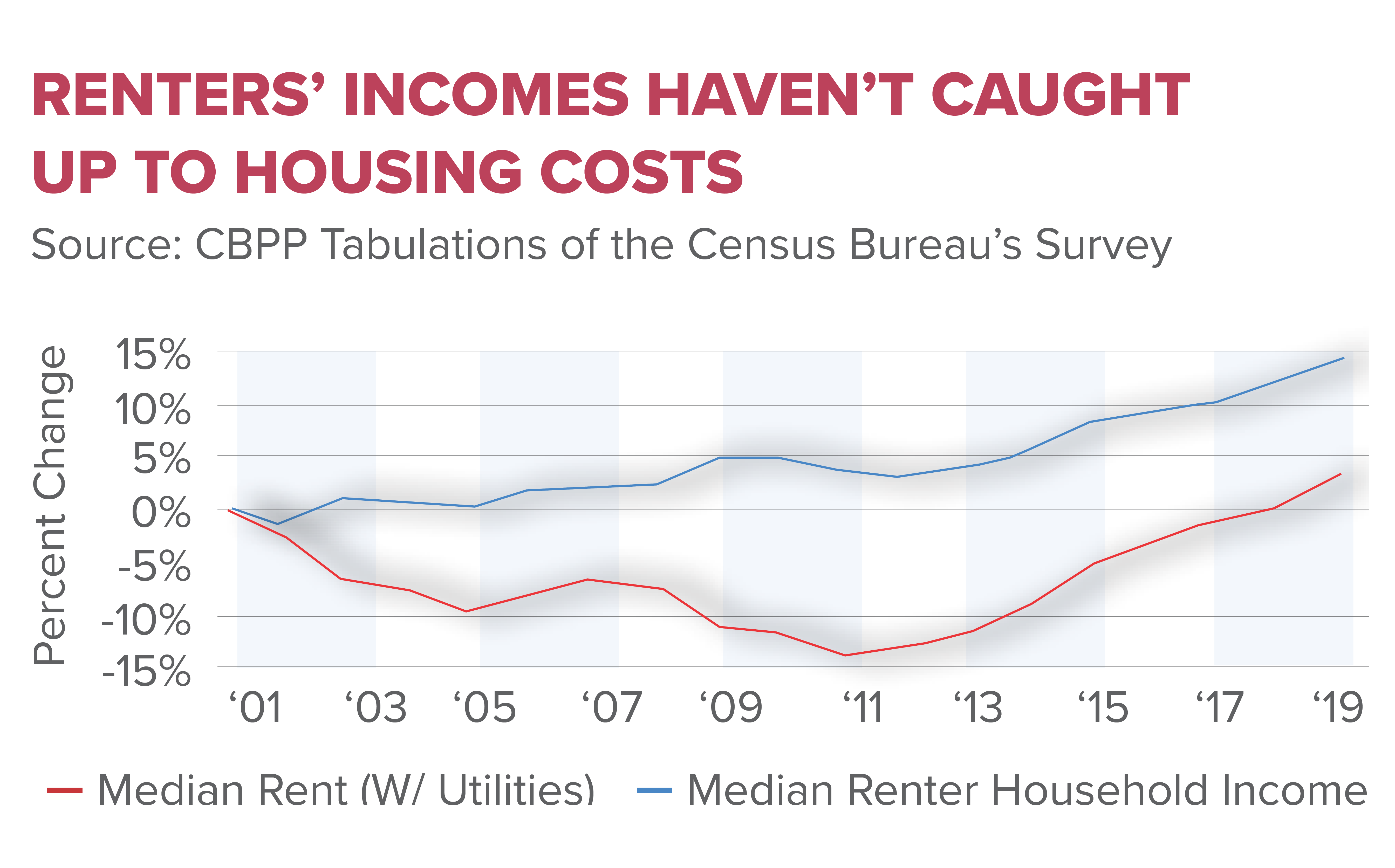
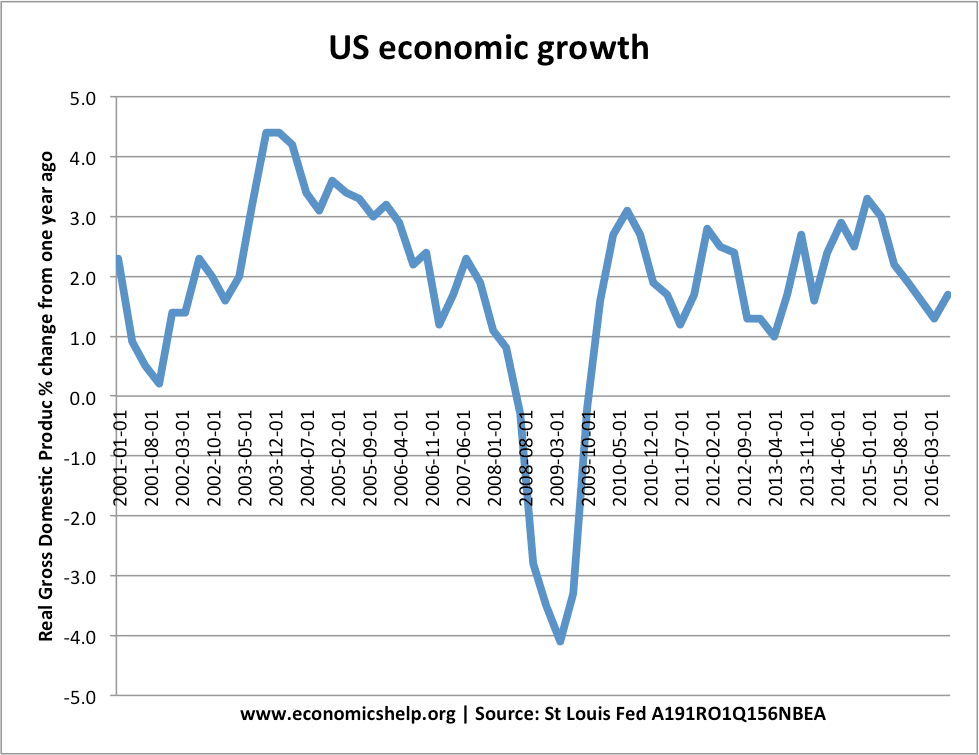
The interconnection between unemployment and entrepreneurialism has been a recurring theme throughout history, especially in times of economic distress. As Erik Baker discusses, periods of substantial job loss have often given rise to a surge in entrepreneurial activity as individuals look to create their own opportunities amidst uncertainty. In stark economic climates, many are pushed to explore self-employment as a viable alternative, demonstrating resilience in the face of adversity.
However, while entrepreneurialism may respond to unemployment, the relationship is complex. Not everyone has access to resources or networks to launch their ventures successfully. Educational initiatives and support systems are paramount to empower individuals who wish to transition into entrepreneurship, ensuring that economic downturns do not stifle potential innovation. Thus, fostering an inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem can counteract high unemployment rates while cultivating an enterprising spirit in society.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is entrepreneurialism and how can it influence modern work culture?
Entrepreneurialism refers to the mindset and practices of individuals who seek to create and innovate within various industries, transforming the way we engage with work. In modern work culture, it encourages self-employment, flexibility, and a freelance economy, allowing people to make their own job opportunities and embrace their unique skills.
How does the entrepreneurial mindset contribute to self-employment?
The entrepreneurial mindset fosters creativity, resilience, and resourcefulness, enabling individuals to create their own job roles rather than conforming to traditional job structures. This shift not only supports self-employment but also empowers people to explore freelance opportunities that align with their passions and expertise.
What are the benefits of embracing entrepreneurialism in today’s economy?
Embracing entrepreneurialism in today’s economy can lead to greater job satisfaction, increased autonomy, and financial independence. It allows individuals to navigate the freelance economy effectively, adapt to changing market demands, and create meaningful work experiences that reflect personal aspirations.
How has entrepreneurialism changed the traditional workforce?
Entrepreneurialism has shifted the traditional workforce by introducing concepts like self-employment and the gig economy, where individuals take on multiple roles or projects. This change reflects a modern work culture that values flexibility, innovation, and personal fulfillment over conventional corporate job paths.
What does it mean to be a solopreneur in the context of entrepreneurialism?
Being a solopreneur means operating as a one-person business, where an individual leverages their skills and creativity to offer products or services directly to clients. This embodies the entrepreneurial spirit by making self-employment the primary focus and embracing the challenges of running an independent enterprise.
How can individuals thrive in the freelance economy as self-employed entrepreneurs?
To thrive in the freelance economy, self-employed individuals should develop a strong personal brand, network effectively, and leverage digital platforms for visibility. Additionally, adopting an entrepreneurial mindset that embraces learning and adaptation can be crucial in navigating the ever-evolving market landscape.
What role does risk play in entrepreneurialism and modern work culture?
Risk is intrinsic to entrepreneurialism and modern work culture, as individuals often face uncertainty and potential failure in their pursuit of innovation and independence. Recognizing and managing these risks can foster resilience, encouraging entrepreneurs to learn from challenges and maintain a forward-thinking perspective.
How does the history of entrepreneurialism inform our current understanding of work?
The history of entrepreneurialism reveals how societal shifts, such as economic stress and technological advancements, have influenced our understanding of work. By examining past trends, we can better appreciate the value of self-employment and the entrepreneurial mindset in shaping a more adaptive and fulfilling modern work culture.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Entrepreneurialism is now pervasive in American work culture, encompassed by various roles such as entrepreneurs, intrapreneurs, solopreneurs, and gig workers. |
| The concept of entrepreneurialism has evolved since the end of the 19th century, becoming more prominent during times of economic stress. |
| Baker traces the shift from a traditional work ethic to one focused on personal ambition and skill application. |
| Historical influences, including self-help literature, have shaped the entrepreneurial mindset emphasizing specialization and innovation. |
| Mid-20th century, entrepreneurialism became a response to economic challenges in cities facing decline, with a broader definition encompassing all levels of society. |
| In contemporary times, entrepreneurialism glorifies risk-taking, contributing to stress and anxiety among workers, reflecting a need for a constant forward-looking attitude. |
Summary
Entrepreneurialism has transformed the American work landscape, linking personal ambition with the changing economic structure. As individuals navigate the pressures of modern work, the drive to embrace entrepreneurialism reflects not only a response to job scarcity but also a cultural shift towards valuing personal engagement in one’s career. Embracing this mindset, despite its challenges, may lead to a more fulfilling and self-directed professional life.